Teak
Denominación.
• Scientific name: Tectona grandis L. F.
• Spanish: Teka
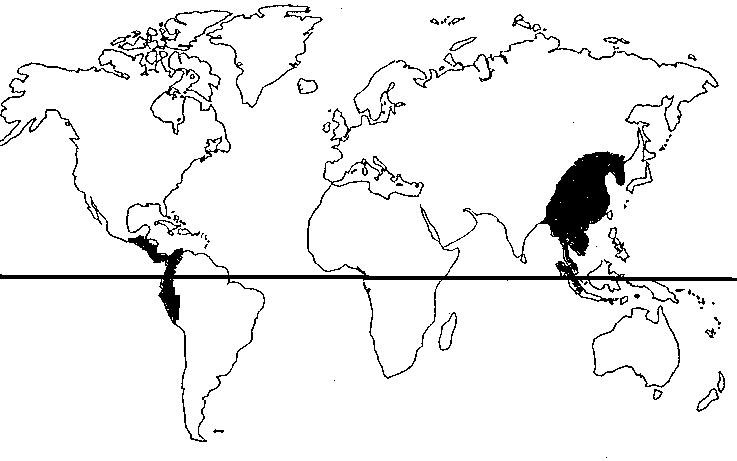
Provenance
Description of the wood
• Sapwood: Yellowish to grayish white.
• Heartwood: Yellowish brown to dark brown with frequent dark gray streaks.
• Fiber: Straight.
• Grain: Medium to coarse.
• Singularities: Greasy wood with calcareous and silica deposits.
Impregnation
• Sapwood: Little impregnable
• Heartwood: Non-impregnable
Mechanization
• Sawing: Without further problems those of its high silica content that quickly wears down the tools and causes allergy to workers.
• Drying: Slow speed at very lenla. Small risks of deformations and fendas.
• Planning: No problems other than its abrasiveness. Suitable for bending.
• Gluing: High difficulties due to its high content of oleoresins, especially if alkaline glues are used.
• Nailing and screwing: Requires pre-drills.
• Finishing: The difficulties already indicated in the gluing.
Applications
• Furniture and fine cabinetry of interior and especially of exterior. Curved and turned furniture.
• Carpentry of intenor and especially exterior; doors, windows, floors and coatings.
• Shipbuilding.
• Decorative plates.
Mechanical properties
• Resistance to static flexion 1,020 kg/cm2
• Elasticity module 110,000 kg/cm2
• Resistance to compression 630 kg/cm2
Notes
- The photos are by Teka Asiatica.
In some countries of Africa and South America there are plantations of trees of this species. Being fast growing, with very separate growth rings, the characteristics and benefits are lower, it has less fat so its endurance in the open is lower and has wide dark meshes.


